个人感觉监督学习任务是给定输入我们预测一个输出,连续或者离散的,是从输入到输出的映射;而强化学习则更高一层,是主体和环境之间的交互,是一个连续的决策过程:主体对当前环境做出最佳决策,这个决策的过程也可以视为预测任务,去预测一个最佳输出,不断重复这个过程。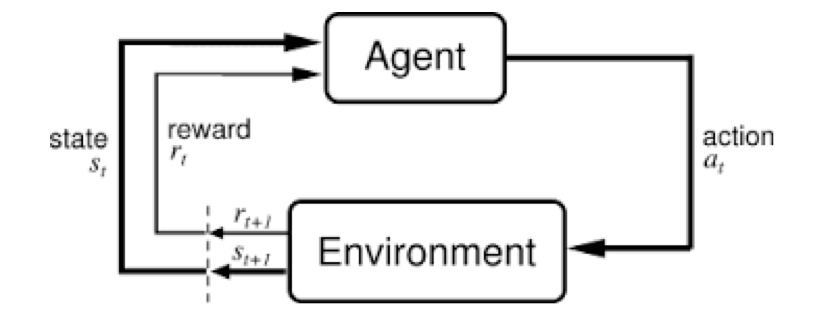
如视频中所言,本质上强化学习这个任务可以包含监督学习。
¥
支付方式
请使用微信扫一扫 扫描二维码支付
请使用支付宝扫一扫 扫描二维码支付
个人感觉监督学习任务是给定输入我们预测一个输出,连续或者离散的,是从输入到输出的映射;而强化学习则更高一层,是主体和环境之间的交互,是一个连续的决策过程:主体对当前环境做出最佳决策,这个决策的过程也可以视为预测任务,去预测一个最佳输出,不断重复这个过程。
如视频中所言,本质上强化学习这个任务可以包含监督学习。
1、强化学习本质上就是给出了一种可以处理决策的数学框架
2、将神经网络与强化学习结合,TD gammon就是结合两者得到一个价值函数。变换的算法是拟合值迭代
3、端到端学习:需要高层次的抽象
4、 深度强化学习的挑战:奖励函数到底是什么样子的
模仿学习
预测,学习机制以及简单规则的定义
如何突破策略游戏
循环神经网络-》记忆性强化学习
第一讲中展示的深度强化学习在机械手控制、供应链管理、交通协调方面的示例对我的启发很大,之前我认为解决大系统问题最好是将大系统的所有规律方程都列出来,然后为一个目标求出一个解,但是可能有的时候求出一个全解,需要的计算量可能满足不了。这里给系统中每个个体都有一个强化学习的自主能力,通过训练,最后每个个体遵从它在与环境交互过程中学习到的规则达到了整个系统的协调。这类似于群智能算法,群智能算法要设定每个个体的规则,然后每个个体按照其设定的规则迭代最终寻到较优解。而这里应用深度强化学习所能够学习到的规则是在于环境交互中学到的。
Learning as the basis of intelligence
deep reinforcement learning
a.from supervised learning to decision making
b.model_free algorithms
c.advanced model learning and prediction
exploration
d.transfer and multi-task learning, meta-learning
what is reinforcement learning?
adapt
deep learning helps us handle unstructured environments.(不断变化的)
reinforcement learning provided a formalism for behavior.
interaction between agent and environment
decisions(actions)-consequences(observations\rewards)
end-to-end learning
robotic control pipeline:
obserations-state estimation-modeling prediction-planning-low-level control-controls
problems:
beyond learning from reward
maximizing rewards
advanced topics: inverse reinforcement learning, transfer learning
where do rewards come from?...
Are there other forms of supervison?
learning from demonstrations:copy, infer
learning from observing the world:predict, unsupervised learning
learning from other tasks:transfer learning, meta-learning
learning as the basis of intelligence
single algorithm do?
interpret rich sensory inputs 理解
choose complex actions 选择动作
why deep reinforcement learning?
deep can process complex sensory input
reinforcement learning can choose complex actions.
强化学习在动物大脑中存在
challengings?
humans can incredibly quickly
humans can reuse past knowledge
no clear what the reward function should be
not clear what the role of prediction should be
使用一个通用的算法和环境交互
instead of trying to produce a program to simulate the adult mind, why not rather try to produce one which simulates the child's? If this were then subjected to an appropriate course of education one would obtain the adult brain.-----Alan Turing
介绍了强化学习的背景以及我们如何构建智能设备,后面介绍了课程作业,介绍了架构环境Tensorflow,继续学习!
强化学习提供用来做决策的数学框架。
与深度学习一样 ,deeprl实现端到端的学习。
展望深度强化学习的未来。
深度学习帮助我们处理 unstructured 环境(不能提前预测的,经常变的),例如图像识别、自然语言处理、语音识别等。
是端到端的训练,而不是多步分别优化
强化学习提供了 decision making 的框架。
深度模型 使得 强化学习可以端到端的解决复杂问题。
现在研究DRL的原因:深度学习的进步 + 强化学习的进步 + 计算能力的进步
历史:
reward的设置, 直接reward是非常少的,reward从何而来?除了reward, 还可以有其他的 supervision
猜想:有一个统一的算法处理各种学习
证据:人的不同感觉可以相互转换,例如可以用舌头看,雪貂的听觉皮层可以处理视觉信息(经过足够时间训练)
DRL能做什么,不能做什么?
能做:
挑战(开放问题):
- Deep: can process complex sensory input and can also compute really complex functions
- Reinforcement learning: can choose complex actions
一、介绍了课程内容大纲:
(1)从监督学习到决策问题,模仿学习;
(2)model-free,Q-learning、policy gradients, AC;
(3)model-base 和一些高级问题;
(4)exploration(搜索);
(5)迁移学习、多任务学习、meta-learning(元学习);
(6)开放问题、研究报告、讲座。
二、介绍了什么是强化学习和为什么要用强化学习(有什么优点)。